Mouth Cancer: Understanding Its Impact and Prevention
Written by Agata Myszka
Medically reviewed and edited by Dr Said Qabbaah, MBBS, MBA
Scientifically reviewed by Dr Angela Pine, BSc, MSc, PhD1
Mouth cancer affects a significant number of people in the UK, with over 10,000 new cases diagnosed every year, leading to the death of more than 30% of those affected.1
Worldwide, there are more than 650,000 new cases of mouth cancer annually, and the incidence is predicted to get higher in the future. However, research suggests that little is known by the general public about the signs, symptoms, and risk factors for developing mouth cancer.
What is mouth cancer?
Mouth cancer (also known as oral cancer) is a type of cancer that can affect any part of the mouth:2
-
- Inner lining of the cheeks and lips (buccal mucosa)
- Front 2/3 of the tongue
- Gums
- Floor of the mouth
- Roof of the mouth (hard palate)
- Area behind the wisdom teeth (retromolar trigone)
- Lips
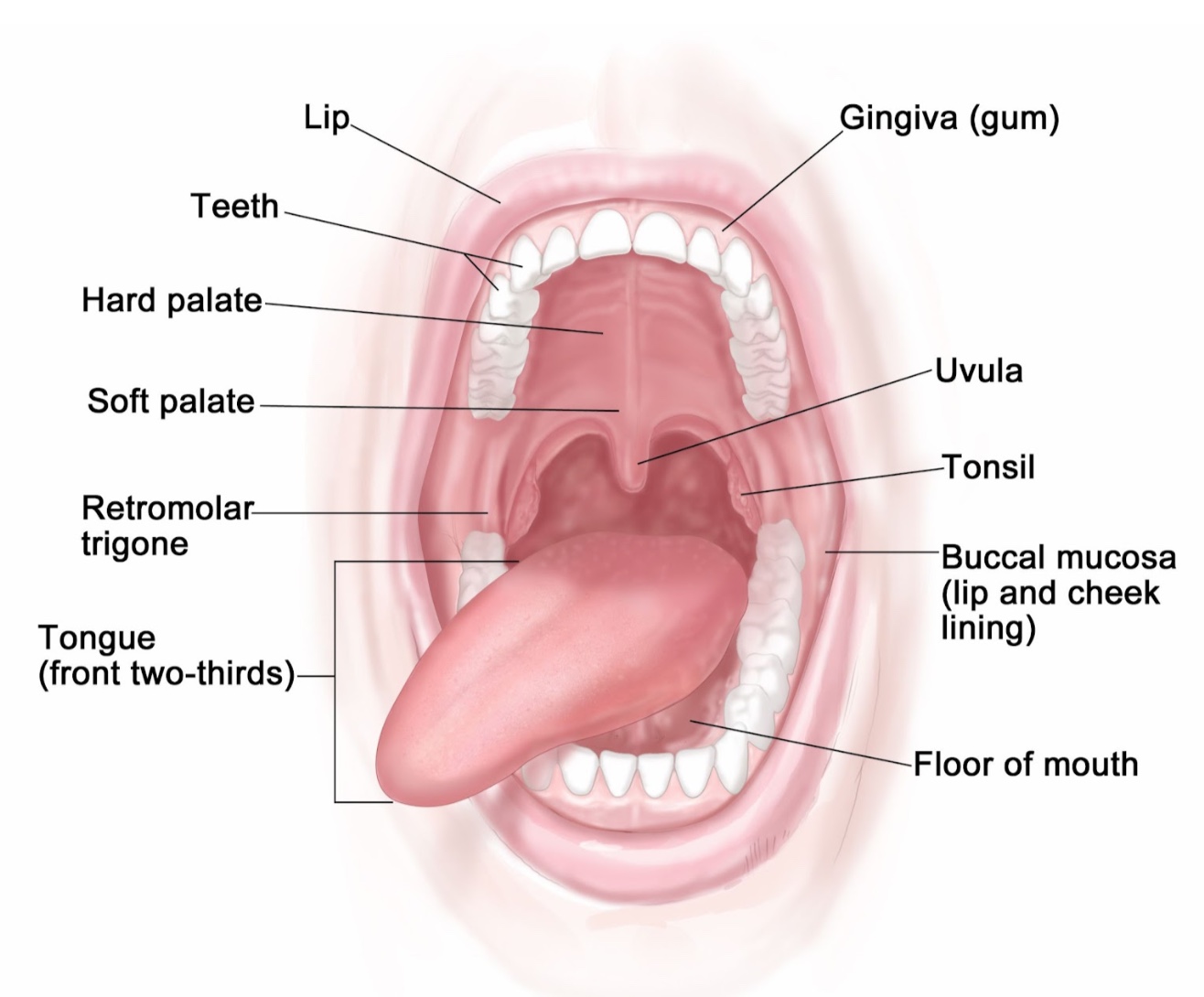
Figure 1 Anatomy of the oral cavity3
Mouth cancer: Risk factors
While it is true that anyone can develop mouth cancer, certain risk factors can make this more likely, such as:1,4
Tobacco use: This represents the main risk factor for mouth cancer and involves the use of any form of tobacco product. However, while this is recognised as the principal risk factor, non-smokers can still develop mouth cancer too. In fact, up to 25% of mouth cancer cases have no significant risk factors associated with it.
Alcohol consumption: Consuming excessive amounts of alcohol is associated with a fourfold increase in the risk of developing mouth cancer. Drinking and smoking together can make mouth cancer up to 30 times more likely to develop.
Human papillomavirus (HPV): Oral HPV infection, which is transmitted through oral sex, is associated with an increased risk of mouth cancer, and could overtake tobacco and alcohol as the main risk factor in the near future.
Chronic gum disease: Persistent inflammation or irritation of the gum, which can be caused by poor oral hygiene or ill-fitting dentures, may contribute to the development of mouth cancer.
Sun exposure: Prolonged exposure to sunlight without adequate protection can increase the risk of lip cancer.
Poor diet: Excessive intake of unhealthy foods and beverages that lack essential nutrients, along with the insufficient consumption of fruits and vegetables, can increase the risk of developing mouth cancer.
Age: The risk of developing mouth cancer increases with age, particularly after the age of 55.
Gender: Men are twice more likely to develop mouth cancer compared to women; it affects an average of 1 in 55 men, and 1 in 108 women.
Mouth cancer: Its relation with HPV
HPV infection, specifically with high-risk HPV type 16 can cause healthy cells within the oral cavity to become abnormal, which may eventually develop into cancer over time.4
However, it is important to note that while HPV infection is a risk factor for mouth cancer, not everyone with HPV infection will develop cancer. It is still very important to seek medical attention if there are any persisting symptoms or when something feels unusual in order to prevent possible health complications that could result from late detection and diagnosis.
Mouth cancer: Common signs and symptoms
The following is a list of the most common signs and symptoms of mouth cancer:1,2
- A mouth ulcer that lasts more than 3 weeks
- A persisting red or white patch inside the mouth
- Difficulty swallowing
- Difficulty speaking or persistent hoarseness (croaky voice)
- A persisting lump inside the mouth, lips, head, or neck
- Pain, numbness, or bleeding inside the mouth
- Unexplained loosening of teeth
It is important to note that the above symptoms are not exclusively caused by mouth cancer, and can be due to a range of other health conditions.
It is still highly advisable to get immediate medical attention if there is any reason for concern or doubt in order to prevent possible health complications. This is because the early detection of mouth cancer is crucial for beating the disease, as treatment during the early stages will be far more effective.
However, if it is left undetected or untreated, it could lead to the late discovery of mouth cancer when it has already reached an advanced stage, making treatment much more difficult and resulting in a situation where it can even be life-threatening.
Mouth cancer: Prevention measures
The best way to protect yourself against mouth cancer is to avoid the key risk factors that increase its chances of developing in the first place. This involves making simple but effective lifestyle choices that can be incorporated into daily life and can play a crucial role in the protection against this potentially life-threatening disease.
In addition, having access to preventative and early detection programmes is vital to help prevent the development of mouth cancer and its related complications5.
Some of the risk factors that can be controlled include limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding the use of tobacco products which can significantly help reduce the risk of developing mouth cancer.1,5
Other important lifestyle factors to consider include: engaging in regular physical exercise, maintaining good oral hygiene, and eating a healthy balanced diet containing a variety of nutritious foods, including fruits and vegetables, that provide a rich source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Avoiding excessive sun exposure is also very important in the protection against lip cancer which can be achieved by doing certain things such as using sunblock, wearing a hat, and limiting the time spent under direct sunlight, especially during peak hours in the summer.
Additional measures are aimed at reducing the risk of oral HPV infection, and help offer protection against the development of mouth cancer. These preventative measures include HPV vaccination and the practice of safe sex with the proper use of condoms and dental dams.
10zyme: Advancing women’s health
We’re developing a groundbreaking self-test with instant results to detect the main cause of cervical cancer: high-risk HPV. Detecting infections early prevents cancer ever developing.
By enabling self-testing, we aim to empower women, overcome stigma and anxiety, and help eliminate a disease killing hundreds of thousands a year globally. See our Education Section to find out more.
Please follow and support us on social media: LinkedIn, Instagram, and TikTok.
References:
- Mouth Cancer Foundation. (2024). Facts and figures about mouth cancer. [Online]. Available at: https://www.mouthcancerfoundation.org/ (Accessed 15/03/2024)
- National Health Service (NHS). (2023) What is mouth cancer? [Online]. Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/mouth-cancer/what-is-mouth-cancer/ (Accessed 15/03/2024)
- National Cancer Institute. Oral cavity. [Online]. Available at: https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/oral-cavity (Accessed 15/03/2024)
- Cancer Research UK. (2022). Mouth and oropharyngeal cancer – risks and causes. [Online]. Available at: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/mouth-cancer/risks-causes (Accessed 15/03/2024)
- World Health Organization (WHO). (2023). Comprehensive assessment of evidence on oral cancer prevention released. [Online]. Available at: https://www.who.int/news/item/29-11-2023-comprehensive-assessment-of-evidence-on-oral-cancer-prevention-released-29-november-2023 (Accessed 15/03/2024)


3 thoughts on “Mouth Cancer: Understanding Its Impact and Prevention”